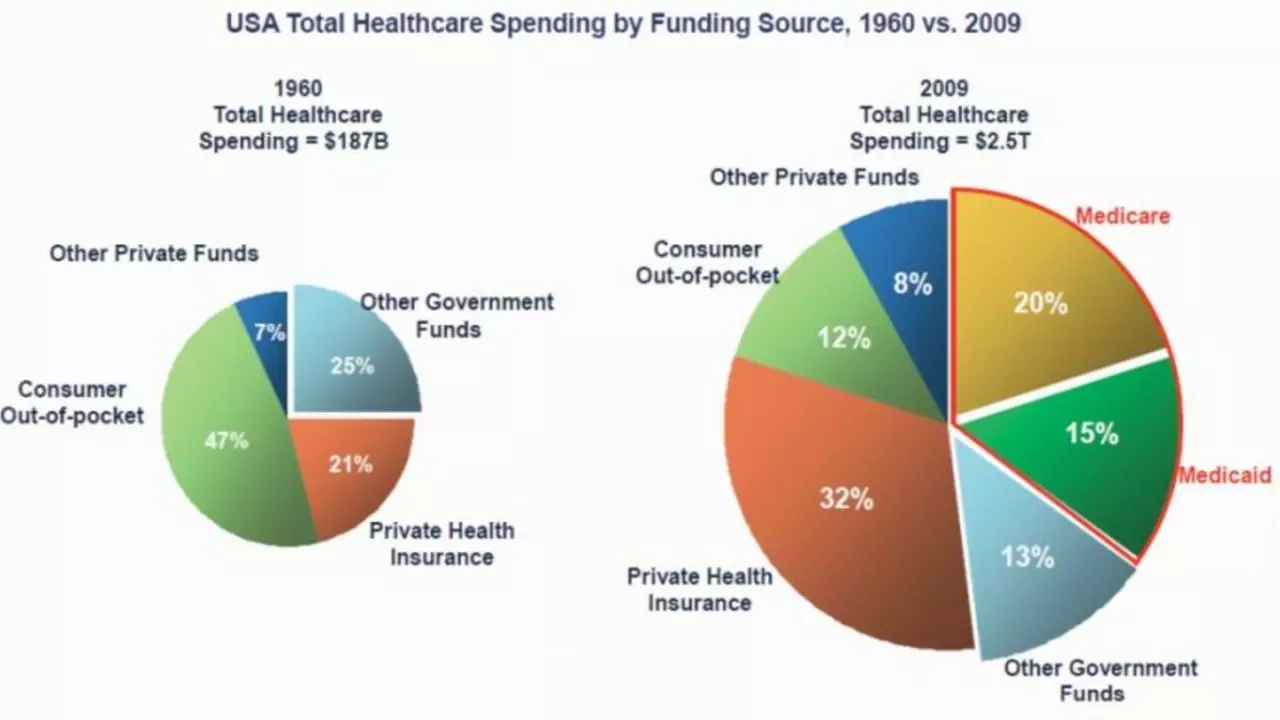
What are the types of health insurance coverage in America?
Understanding the Basics of Health Insurance Coverage
In the simplest terms, health insurance is a contract between the insurer and the insured, where the insurer agrees to pay a portion or all of the insured's healthcare costs in exchange for regular premium payments. This contract is also referred to as a health insurance policy. In the United States, there are several types of health insurance coverage, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. The type of coverage you need will depend on your personal circumstances, including your health, age, budget, and lifestyle.
As someone who has navigated the complexities of the American health insurance system, I've learned a thing or two about the different types of coverage available. From private insurance to government-funded programs, every American has options when it comes to protecting their health. In this article, I will break down these options to help you understand what type of coverage might be right for you.
Private Health Insurance Coverage
Private health insurance is often provided through employers, but you can also purchase it individually. It typically covers a portion of your health care costs in exchange for a monthly premium. The coverage provided by private insurance varies widely, depending on the plan's details and your employer's contributions.
There are three main types of private health insurance: Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Point of Service (POS) plans. HMOs require you to use their network of doctors and hospitals. PPOs allow you to use out-of-network providers for a higher cost, while POS plans are a mix of HMO and PPO plans.
Government-Funded Health Insurance Programs
Several government-funded health insurance programs are available in the United States. These include Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP).
Medicare is a federal program that provides health coverage for people aged 65 or older or with certain disabilities. Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage for some low-income people, families and children, pregnant women, the elderly, and people with disabilities. CHIP provides low-cost health coverage to children in families that earn too much money to qualify for Medicaid.
Managed Care Plans
Managed care plans are a type of health insurance where the insurer contracts with a network of healthcare providers to deliver care for members at lower costs. These plans focus on controlling costs and improving quality.
In a managed care plan, you typically choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates your care. This includes making referrals to specialists when needed. The three most common types of managed care plans are Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Point of Service (POS) plans.
High-Deductible Health Plans
High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) are insurance policies with higher deductibles but lower premiums. These plans may be combined with health savings accounts that allow individuals to pay for certain medical expenses with pre-tax money.
HDHPs can be beneficial for people who are generally healthy and don't require frequent medical care. However, if you become seriously ill or injured, you may have to pay a significant amount of money out-of-pocket before your insurance starts to cover costs. It's important to consider your health and financial situation before opting for a high-deductible plan.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Health Insurance Coverage
Understanding the different types of health insurance coverage in America is crucial for making an informed decision about your healthcare. Whether you choose a private insurance plan, a government-funded program, a managed care plan, or a high-deductible plan, your choice should be based on your unique health and financial needs.
Remember, health insurance is not a one-size-fits-all solution. What works best for one person may not work for another. Therefore, take the time to research and understand your options. If needed, consult with a health insurance professional who can guide you through the process.